We have already discussed the price determination of
a commodity whose demand and supply curves are given, but generally demand and
supply keeps on changing, resulting in shift in demand (factors like income, tastes and preferences etc.) and supply( change in technologies, input
prices etc.) curves.
Let us now see the effect of change in
demand and supply, on the equilibrium price and quantity.
Change in demand and Market Equilibrium
Change in demand
has two aspects:
1) Increase in
demand- demand curve shift to the right
2) Decrease in
demand- demand curve shift to the left
Increase in demand:
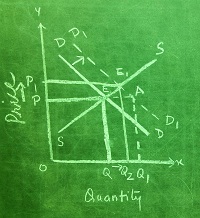 |
| demand supply |
In the above
diagram, DD and SS are the initial demand and supply curves. Equilibrium is
struck at E, P and Q is the initial equilibrium price and quantity.
In case of increase
in demand:
a) Demand Curve
shift to the right. D1D1 is the new demand curve, supply
curve remains the same.
b) Quantity demanded
will be OQ1 but the supply will remain at OQ. An excess demand
(shortage) occurs at the initial price.
c) Competition
among consumers and producers causes the price to rise to OP1.
d) As price rises,
the quantity supplied rises (law of supply, extension of supply) from E towards
E1. Quantity demanded falls (law of demand, contraction of demand)
from point A towards E1.
e) The process of
contraction of demand and extension of supply continue until two becomes equal,
after that there is no more tendency for either price or quantity to change.
Thus, an increase in demand for a commodity causes an increase in
both equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity bought and sold.
 |
| Market Equilibrium |
In the above
diagram, DD and SS are the initial demand and supply curves. Equilibrium is
struck at E, P and Q is the initial equilibrium price and quantity.
In case of decrease
in demand:
a) Demand Curve
shift to the left. D1D1 is the new demand curve, supply
curve remains the same.
b) Quantity
demanded will fall to OQ2 but the supply will remain at OQ. An
excess supply (surplus) occurs at the initial price.
c) Competition
among consumers and producers causes the price to fall to OP1.
d) As price falls,
the quantity supplied falls (law of supply, contraction of supply) from E
towards E1. Quantity demanded rises (law of demand, extension of
demand) from point A towards E1.
e) The process of
extension of demand and contraction of supply continue until two becomes equal,
after that there is no more tendency for either price or quantity to change.
Thus, decrease in demand for a commodity causes a decrease in both
equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity bought and sold.
Change in Supply and Market Equilibrium
Change in supply
has two aspects:
1) Increase in
supply - demand curve shift to the right
2) Decrease in
supply - demand curve shift to the left
Increase in supply:
 |
| Market Equilibrium |
In the above
diagram, DD and SS are the initial demand and supply curves. Equilibrium is
struck at E, P and Q is the initial equilibrium price and quantity.
In case of increase
in supply:
a) Supply Curve
shift to the right. S1S1 is the new supply curve, demand
curve remains the same.
b) Quantity
supplied will be OQ1 but the demand will remain at OQ. An excess
supply (surplus) occurs at the initial price.
c) Competition
among consumers and producers causes the price to fall to OP1.
d) As price falls,
the quantity supplied falls (law of supply, contraction of supply) from A
towards E1. Quantity demanded rises (law of demand, extension of
demand) from point E towards E1.
e) The process of
extension of demand and contraction of supply continue until two becomes equal,
after that there is no more tendency for either price or quantity to change.
Thus, an increase in supply for a commodity causes a decrease in
equilibrium price and increase in equilibrium quantity bought and sold.
Decrease in supply:
 |
| Market Equilibrium |
In the above
diagram, DD and SS are the initial demand and supply curves. Equilibrium is
struck at E, P and Q is the initial equilibrium price and quantity.
In case of decrease
in supply:
a) Supply Curve
shift to the left. S1S1is the new supply curve, demand
curve remains the same.
b) Quantity
supplied falls to OQ1 but the demand will remain at OQ. An excess demand
(shortage) occurs at the initial price.
c) Competition
among consumers and producers causes the price to rise to OP1.
d) As price rises,
the quantity supplied rises (law of supply, extension of supply) from A towards
E1. Quantity demanded falls (law of demand, contraction of demand)
from point E towards E1.
e) The process of
extension of demand and contraction of supply continue until two becomes equal,
after that there is no more tendency for either price or quantity to change.
Thus, decrease in supply for a commodity causes an increase in
equilibrium price and decrease in equilibrium quantity bought and sold.

No comments:
Post a Comment